Multihull Keels and Daggerboards

Fountaine Pajot BELIZE 43 resting on her keels, showing good bridge deck height
Uncovering the compromises of both underwater appendages and analyzing their disadvantages and merits.
Man has learned much from nature, and sailboats and their underwater appendages are one of the areas that we have applied what works and what doesn’t. As we all know, boats – as most things in life- are compromises and often we are prepared to make concessions in one area in order to gain an advantage in another. Not only should this brief discussion illustrate the basic virtues and drawbacks of daggerboards and mini keels on multihulls, but also point out their active and passive safety aspects.
Most multihulls in todays marketplace come in two varieties. By far the vast majority of the production cruising catamarans (about 90%) are keelboats and have low aspect ratio, unballasted keels. These well known French, Australian or S.African boat manufacturers market their boats for private ownership and the charter industry and make a great product. Without sounding too general, these boats have very spacious interiors and are perfectly adaptable for live aboard families or the charter trade. This multi million dollar charter industry, has an obvious influence on the requirements and design of their charter fleet, which further has a trickle down effect to other builders who also market their cats for private ownership. Design parameters for these charter cats are often centered around 2 week multiple family vacations in the steady Trade Winds and day sails between closely spaced islands of the Caribbean. The features of these keel catamarans obviously put less demand on pure sailing performance or extreme upwind sailing characteristics, but rather try to please by offering solid construction, live aboard comfort and simple and reliable handling characteristics.

Fountaine Pajot BELIZE 43 resting on her keels, showing good bridge deck height
The other type of multihull is the catamaran with articulating daggerboards or centerboards. Centerboard and daggerboard multihulls both share the same basic concept, except their deployment and storage relies on different principles. The daggerboard lives in a scabbard, or daggerboard trunk. It moves up and down, vs. a pivoting centerboard, which is raised and lowered around a massive pin. High aspect ratio daggerboards are by far the most efficient foils. They have none of the problems associated with centerboards, which when fully lowered are only braced by a small area on top. When going upwind in a hurry, loads on the trunk act as a giant lever, which constantly work to spread the trunk apart. This is the reason why it is recommended to operate foils as pairs in heavier conditions to divide the loads. Also the large area of the remaining centerboard slot creates a lot of unwanted turbulence making them unpopular for performance minded sailors. Lastly declining popularity of the centerboarders can also be lead back to the often large intrusion on the interior space the trunks create. Although the Gemini catamaran is a good example of a very popular and well thought out production catamaran, there are few other mass produced centerboarders around. It should be noted that one great advantage centerboards have vs. any other underbody configuration is that they theoretically retract when colliding with an object. In spite of this, most offshore or performance orientated sailors clearly favor daggerboards or low aspect ration keels.
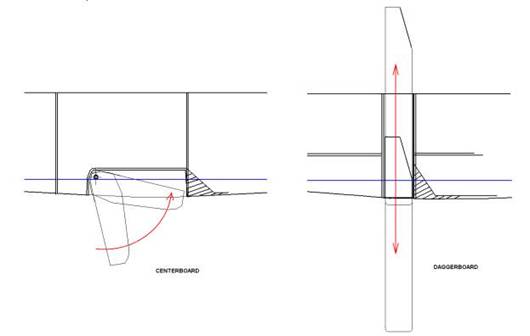
Illustration A
Daggerboard catamarans have several advantages over their keel counterparts, some of which are well known and others that are more subtle and sometimes only recognized by people who have used them. Active safety aspects are advantages created by speed and the ability to retract underwater appendages.
I am a firm believer of “faster” rather than “slower” on ocean going performance multihulls. Many people might say, going fast is only for racers. But lets think about this. The ability to reduce exposure time through speed is invaluable for cruisers. If say on a transatlantic passage you can shave off 5 days you have already increased your safety factor, in some cases, by 25%. Not being a “sitting duck” is a nice thing indeed. By being able to have the choice, bad weather can be avoided, which can sometimes lead to a negative spiral of incidences. In general, especially on long passages, a daggerboard cat will have the edge on speed over her keel counterpart.
Lets face it, we are all in it for the fun of sailing as famed designer Francis L. Herrshoff said: “The fun of sailing is directly proportional to the speed of sailing”. Maybe this is the reason he designed Amaryllis, his revolutionary catamaran, which was later banned from racing. Generally speaking daggerboard catamarans will always be slightly faster than their keel equivalents. The speed advantage of most daggerboard catamarans vs. keel catamarans though is often exaggerated. On a typical day sail a well trimmed and tuned keel cat will only be slightly slower than a daggerboard cat.
Multihulls lack the feeling of being in the “groove”, which monohull sailors enjoy. Effortless high average speeds, acceleration and sustained high velocity surfs is something fast multihulls compensate with. It should be noted that anything (even a barn door) surfs in the right conditions. Even keel catamarans can surf at speeds up to 30 knots down large seas.
Upwind Advantages: Depending on sea state going upwind, daggerboard catamarans vs. their keel relatives will point up to 5 degrees higher and also experience 2-5 degrees less leeway, which isn’t much one would think. But in an uncomfortable 100 mile beat this ads up to being more than 17 miles closer to your destination! (Illustration B).
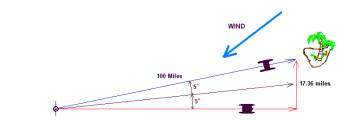
Illustration B
sin A=a/c
(sin A) c =a
(0.1736) * 100 = a
a = 17.36 miles
Lets take a 45’ catamaran: the lift (to windward) generated by a daggerboard is almost twice that of a low aspect ratio keel and the drag with the board all the way down would be almost 20% less. The most recent generation cats with large beams and stately bridge deck houses benefit especially from high lift foils, since the windage of their projected area can ad up quickly. The same cats with keels usually suffer from excessive leeway and sideslip. Keel cat’s however, especially in a calm sea state, lessen this disadvantage as boat speed and flow over their keels increases.
Reaching and Running Deep: When running deep in fresh conditions the fixed could act as a brake, that one cannot disengage. Since they cannot be retracted, their volume and resistance slows the boat’s progress and in combination with the forward pressure of the sails forces the bows down. This is especially the case with catamarans that have long bridgedecks, heavy extremities and low volume- fine bows. The bigger the friction in the water, the bigger the pressure on the mast and the more the boat is burdened. Another neat trick is lifting the daggerboards, one can actually increase apparent wind by pointing up and induce leeway, crabbing faster to ones destination.
Tacking and Helm Feedback: Cruising catamarans are often mistaken to tack slowly and behave sluggishly to movements of the helm. This is certainly true for some heavy keel catamarans and much less so for ones equipped with boards. In complex seas, some of the heavier keel cat’s only option for a safe tack is back winding the jib. Monohulls with only one fin will always tack quicker than multihulls, just as foil equipped catamarans will be more responsive than keel multihulls. Modern hydraulic steering systems are easy to build and with most forward helm stations behind the main coachroof, pose sometimes the only alternative for the builder. Mechanical steering and daggerboards will give the ultimate feedback and fun at the helm…if one is driving at all, since usually the autopilot is engaged for longer legs.

Inclined foils on the Aeroyacht H42 performance catamaran built by Edel
Another advantage of daggerboards is the better maneuverability under one engine. If you loose one engine and retract the board on the hull which has no engine power, but leave the powered hull’s foil down, the boat will turn easier. Because of the retracted foil on the un-powered side there will be much less drag induced turning moment, the boat will be more balanced and the other sides deployed board will provide sufficient bite for “survival” steerage. Especially in high crosswind situations a catamaran with both boards down is much easier to maneuver than one with shallower keels. Usually harbor maneuvers under power are low speed operations, and this is where the high lift capacity of twin boards excel yet again and facilitate handling and precision steerage. Daggerboard cats also can motor a bit faster, since by retracting the foils they have less resistance.
Keel and daggerboard cats usually have less draft than keel monohulls, opening access to shallow anchorages. An advantage daggerboards have, are their gauging characteristics when entering shallow harbors or unknown territory. By lowering them, one actually creates a “safety depth”. When they touch bottom one still has the possibility of raising them, performing a U-turn and getting into deeper water. With fixed- non retractable keels, especially with a monohull, groundings or unplanned bottom encounters could end tragic. At least a monhull can attempt in heeling the boat to reduce draft and re float. This obviously is not an option on a keel cat. If you get stuck in the mud you are dedicated to await the next high tide to get you off. Crashing into a coral reef could be a different story altogether and only a haul out can asses and repair damage. Depending on their design, boards could be rotated or flipped, and even repaired underway. In general daggerboard cats also have less draft than keel multihulls allowing access to even more harbors and anchorages. They can be beached high up for repairs or inspections, increasing the window of exposure time between tides. I know, I once performed a 5 hour long emergency repair on our 43’ catamaran this way, saving 1000’s in yard bills and days of headaches.
It should be notes that keel catamarans however, can be beached just as easy as daggerboard cats. They can be left sitting, high and dry, completely safe on their keels, without having to worry about damaging the hulls or getting debris or sea life stuck into the vulnerable daggerboard trunks.
Bruno Nicoletti is an old friend and one of the most low key-expert sailors I know. He has logged more than 130,000 miles (geriatric miles as he calls them) on his 44’ daggerboard catamaran.. At a recent meeting with him in France we talked about his experiences of his record, double handed – one stop- Southern Ocean circumnavigation at age 63. The French Press compares Bruno to sailing legend Vito Dumas and has published his accounts in an article called: “The Impossible Route”. He explained, that in the Southern Ocean, in the most convoluted conditions he would simply raise both boards, lock the helm to windward and lay a-hull with no sails. “Brumas Patagonia” would safely slide down the steep faces of waves and minimally drift to leeward at about 1 mile per hour while he was either resting or reading. The water spoil of his side wards drift would help keep the edge off cresting waves and often prevent them from breaking (Illustration D) While it was blowing 70 knots and higher he felt very safe and in fact the world around him turned peaceful and quiet. His confidence in this system is impressive: I am currently helping him with sea trials on his new 47 footer for a yet another go at a High Latitude – geriatric- circumnavigation. This time he is planning to take his 78 year old brother and do it non stop !
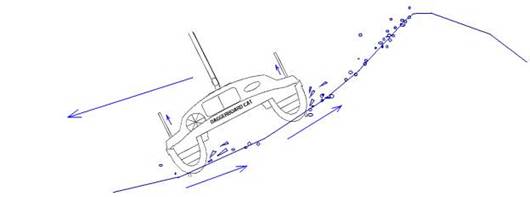
Illustration D
It is not only in the Southern Ocean that one encounters steep, breaking waves. Major capes or the Gulf Stream are notorious for rough conditions where the ability to navigate safely becomes imperative. In these environments any proven and strongly built daggerboard cat would have a slight advantage by lifting her boards, although a well designed keel catamaran could get through unscathed. In extreme weather, and I am talking beyond Force 10, it is very important to enable a catamaran to side-slip rather than encouraging the possibility to trip, and maybe flip. A catamarans behavior in towering side waves is decisive and the possibility to lift underwater appendages is essential, especially if one has lost the ability to steer. The disadvantage of a keel catamaran in huge beam seas is more psychological than real, as these types of vessels typically also slip sideways. In survival conditions or emergencies, the use of parachute anchors, which force the boat into a certain attitude is often thought to be the only answer for most boats. In my mind this tactic is questionable since it puts enormous strains on the boat, is accident prone and renders one helpless when the odd rogue wave from a different direction smacks into the boat. It is better to manage survival conditions, by controlling and slowing the vessel with the use of drogues.
We have learned a great deal from aerospace industry and the trickle down effect to monohull keels. Multihull designers and builders greatly profit from the advanced research, that has been done in the field of NACA sections (National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics) and foil performance. Keels and daggerboards come in a variety of aspect ratios but most are based on low speed foils, which drag/lift characteristics have been optimized. To increase lift even further, some performance catamarans even utilize asymmetrical shaped daggerboards, shaped flat on the outside (leeward) and cambered on the (windward) inside. As they can only be used one at a time asymmetrical boards are somewhat limited in their adaptation for cruisers. (Illustration E)

Illustration E
Since multihulls do not heel, their underwater appendages are more effective in retaining positive flow than their monohull relatives.(this is also the reason why autopilots burn out less often and can be used in heavier conditions on catamarans) As the monohull heels, not only is the upper part partly blanketed by the underbody of the vessel but also flow is lost as the water slips past the angled keel to leeward. (Illustration F) This was especially prevalent on the early IOR monos, which had extremely beamy and shallow bilges and high prismatic coefficient center sections. To compensate for this loss of heel induced flow, monhulls need deep draft keels to make good progress to windward. The keel or daggerboard catamaran on the other hand can more efficiently create lift for the same keel plan view area, not only because it has two vs. one keel, but also through its minimal heel is able to keep its underwater appendages perpendicular in the water.
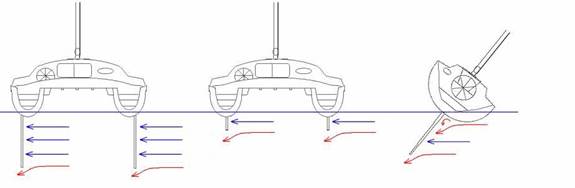
Illustration F
Usually catamaran daggerboards have a higher aspect ratio and are deeper than the equivalent length monohull, since they have the ability to retract them and therefore have no draft considerations. It is therefore not surprising to see that in wind speeds starting at around 10 knots a well designed and sailed daggerboard cat, will often outpoint and outpace a performance monohull. Even well sailed keel catamarans can often arrive earlier at an upwind destination compared to heavy monohulls. The couple of degrees they sacrifice in their ability to point to windward is often made up by their higher speed and VMG (Velocity Made Good). This performance difference increases proportionally to the wind speed and is very noticeable in F.4 conditions and beyond.
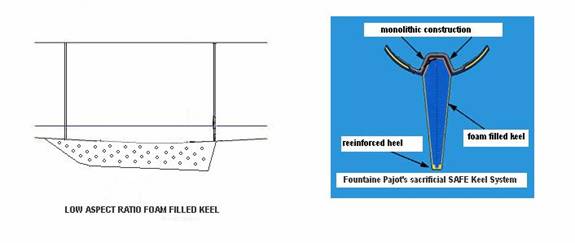
A well known fact and possibly the single biggest psychological deterrent of daggerboard cats is the vulnerability of the boards and trunk in collisions. The true Achilles heel are actually ill constructed and designed trunks, which cause flooding in an impact. This obviously is not the case with keels, which would deflect a minor obstacle, or in case of hitting a container or whale, simply break off. In the case of sacrificial keels, they would sheer leaving the hull completely intact.
Obviously the most critical area in daggerboard design is the construction of the daggerboard trunk. It is usually heavily reinforced with massive gussets, especially at its aft bottom end and extends from the bilge to the overhead. Typical forces on the trunk easily exceed the pressure of the wind on the sails. Dynamic forces of wave action and the shock loads of slamming into seas or solid objects must make this area one of the strongest and best engineered of the entire vessel. Usually the foils are located just aft of the main- mast bearing crossbeam and are somehow tied into this unit to profit from its stiffness. The more “left over” daggerboard remains in the scabbard in the fully down position, the better it is braced, so it is not surprising to see foils that are 18’ long for a 60’ boat. Builders who take their job seriously go through great lengths to make this key area as strong as possible. In a recent conversation with the manager of a reputable French production yard it was pointed out that the daggerboard trunk is engineered and constructed 7 times stronger than the composite board. In case of a violent impact, the foil, which has weak spots designed into it, will snap and leave the daggerboard trunk unscathed. It is a type of sacrificial impact philosophy or a safety fuse, just as it is used on sacrificial fixed keels. The careful engineering and experience necessary in building reliable daggerboard or keel cats stresses the importance of a production yard, which has consistently built them. This aspect should not be taken lightly if one ventures out into the open sea, even if it is only 20 miles offshore.
Often builders of keel cats ad daggerboards to their designs, with the objective to market increased performance and safety. This usually ends up in a compromise, since the hydrodynamic hull requirements of both types could differ substantially, let alone the experience of proper integration, engineering and construction might be lacking altogether. Building with keels does not require the experience, careful construction and engineering which are necessary with retractable foils.
Keels offer advantages, as they do not need to be operated at all. They do their work silently and its usually one less thing to go wrong. On the other hand people who have never sailed with daggerboards think their operation is complicated. In fact they are as easy to use as outhauls or travelers. In normal conditions with 2 people – one pumping the daggerbaords up haul line directly at the board- the other taking up the slack of the up haul, it literally takes 3 seconds to raise a 15’ daggerboard. Single-handed it is a 10 second affair involving 2-3 wraps of the up haul around a winch and 10 cranks. Most boards are slightly heavier than the water they displace and often only weigh 80 lbs. Dropping takes half a second, by simply opening the up haul sheet stopper and easing the foil down. Loads on the boards increase as the speed and pressure builds, so if one has the choice, these maneuvers are usually performed just before tacking. It is a misconception that the operation of foils will depend on the wind speed. It is rather the boat speed, in regards to sea state – which in turn limits progress – which dictates the proper positioning of the daggerboards.
Nothing is perfect and this analysis would be worthless without mentioning the pro’s and con’s of either underwater appendage. Daggerboards, their surrounding structures and systems are more expensive to build, so builders prefer to stay away from them given the choice. In some catamarans, especially smaller ones or ones that have the trunk in the center of the hull, the interior passage in the hulls can be crammed. Lastly it should be mentioned that incorrectly designed and constructed, daggerboards multihulls can be more of a detriment than virtue and in some cases can be extremely dangerous. If the trunks are not massively reinforced and in case of a violent collision one could flood one hull and cause a capsize. In this case one is better off with a well designed and constructed keel multihull than a mediocre or untested one with daggerboards.
Yet daggerboards give you choices, that keels deny you. It is like the new generation of cars with Tiptronic gearboxes, which offer you an automatic transmission with manual override. By physically selecting the proper gear, torque can be adjusted to suit the conditions. It’s the same with the daggerboard equipped catamaran. The boat can be fine tuned to optimize the level of efficiency of the vessels motion through the water. By being able adjust the foils, superior sailing characteristics result in speed and generally more fun on the water. Active safety aspects of reduced exposure time, better maneuverability and shallow draft provide significant benefits.
For safety reasons, most catamarans builders opt for fixed keels and completely separate the keels from the hulls, a feature which preserves and protects the water tightness of the boat in the event of violent impact. Furthermore, if such a situation arises, it makes them easier to repair or replace. Fixed keels require no manipulation, such as daggerboards and give perfect protection to drive shafts, propellers, rudder blades and hull bottoms in the event of grounding. Lastly the absence of a centreboard case means saving of space in the interior of the vessel and usually results in a larger living space.
Back to the birds. We all know the giant Albatross as an extreme example of a sorer that can glide for days in varying conditions, without having to move its wings. This Southern Ocean beast, who calls his home the most inhospitable area on our planet, is better adapted to handle extreme circumstances than any other flying animal. The Albatrosses’ wings are sophisticated in shape, but basically are articulating high aspect ratio foils very similar to daggerboards. Similar to the Falcons “high speed” wings, the Abatross can modify its wings aspect ratio to adjust to the breeze. The designers of the Polynesian multihulls, legendary Viking long ships and American Cargo Schooners understood this too. By adding movable leeway devices, center- or daggerboards, they made their boats more seaworthy and even sailors in the past preferred them over fixed keels.
Today we continue to strive to find the perfect compromise in our vessels to satisfy our most important requirements. We should be extremely thankful to the 1000’s of keel multihulls that have revolutionized the charter industry and many good boats have evolved from this trend. Reputable dagger board catamarans and well designed keel multihulls will continue to be the choice of future generations of serious offshore voyagers. Both offer their advantages and disadvantages and it is important to understand both in order to make the proper choice.
Gregor Tarjan, a trained naval architect and longtime multihull enthusiast is writer of numerous articles for Multihulls Magazine and various other trade publications. He has been involved in Dennis Conner’s “Stars and Sripes” 1984 Americas Cup Campaign, is the founder of Aeroyacht.He is also the co-editor and contributing author of the “Sailors Multihull Guide”, the book by Kevin Jeffrey.